


Next: Experimental Results
Up: Measuring Circular Magnet Rings
Previous: Specification of Task
Description of Magnet Ring Measurement System
The magnet ring measurement system operates as follows.
A magnet ring image is corrected and binarized in the usual way.
(See [6] and section 3.3.)
The resolution of the corrected image is
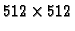 pixels covering
area of
pixels covering
area of
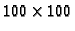 mm.
mm.
Then, the two
contours are extracted and rectified to subpixel precision.
The subpixel rectification procedure is similar to the one used
in [2], with some modifications. The idea is to shift each
contour pixel position along the direction of the intensity gradient
vector so as to find the precise location
where the intensity surface crosses the threshold plane. The gradient
vector is orthogonal to the contour, so each contour point may shift
inwards or outwards depending on the intenisty surface.
The subpixel
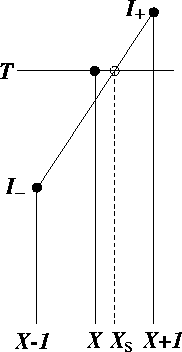
rectification procedure along the gradient direction is illustrated
in figure 16. In this
figure, 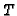 is the threshold,
is the threshold, 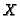 the discrete location of the contour point
obtained without rectification,
the discrete location of the contour point
obtained without rectification, 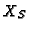 the rectified non-integer location.
The latter is computed by linear interpolation of the intensities
the rectified non-integer location.
The latter is computed by linear interpolation of the intensities
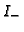 and
and 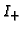 of the neighboring pixels.
of the neighboring pixels.
Figure 16:
Subpixel contour rectification.
 |
The measures computed are defined in accordance with the definitions
given in section 6.1:
- 1.
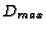 is computed by projecting the contour
to a baseline of changing angle, then selecting the
most extending projection. The angular resolution is
is computed by projecting the contour
to a baseline of changing angle, then selecting the
most extending projection. The angular resolution is 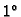 .
.
- 2.
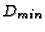 is computed as
is computed as 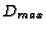 ,
but for the least
extending projection.
,
but for the least
extending projection.
- 3.
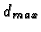 is the same as
is the same as 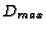 ,
but for the hole.
,
but for the hole.
- 4.
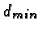 is the same
is the same 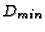 ,
but for the hole.
,
but for the hole.
- 5.
- To compute
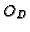 ,
we
consider the diameter as the function of baseline angle.
Then, we take each
pair of diameters separated by
,
we
consider the diameter as the function of baseline angle.
Then, we take each
pair of diameters separated by 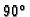 and select the pair for
which the absolute difference of the values is the highest.
and select the pair for
which the absolute difference of the values is the highest.
- 6.
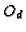 is the same as
is the same as 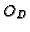 ,
but for the hole.
,
but for the hole.
- 7.
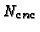 is computed by its definition.
is computed by its definition.
- 8.
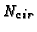 is computed as follows.
The mean radius of the outer contour is obtained via the mean diameter
for all baseline angles. (See Point 1.) Starting from the centroid,
we then compute the absolute deviations of the contour points from
this mean radius. The corresponding area deviations are approximated
by products of the radius deviations and a portion of perimeter spanned
at
is computed as follows.
The mean radius of the outer contour is obtained via the mean diameter
for all baseline angles. (See Point 1.) Starting from the centroid,
we then compute the absolute deviations of the contour points from
this mean radius. The corresponding area deviations are approximated
by products of the radius deviations and a portion of perimeter spanned
at 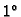 .
Then the sum of the areas is normalized
as defined in (3).
.
Then the sum of the areas is normalized
as defined in (3).



Next: Experimental Results
Up: Measuring Circular Magnet Rings
Previous: Specification of Task
Dmitry Chetverikov
1998-11-16
![]() pixels covering
area of
pixels covering
area of
![]() mm.
mm.
![]() is the threshold,
is the threshold, ![]() the discrete location of the contour point
obtained without rectification,
the discrete location of the contour point
obtained without rectification, ![]() the rectified non-integer location.
The latter is computed by linear interpolation of the intensities
the rectified non-integer location.
The latter is computed by linear interpolation of the intensities
![]() and
and ![]() of the neighboring pixels.
of the neighboring pixels.