

Next: Open problems
Up: Computer Vision IT412
Previous: Stereo matching
Subsections
The algorithm consists of the following steps:
- 1.
- each image is filtered with masks of different resolutions.
- 2.
- zero-crossings in the filtered images, which
roughly correspond to edges, are localized.
- 3.
- matching takes place between pairs of zero-crossings
for a range of disparities up to the width of
the masks' central region.
The uniqueness and continuity constraints are employed.
- 4.
- wide masks can control vergence movements and so
can be used to bring
small masks to come into correspondence.
- 5.
- when a correspondence is achieved, it is stored in
a dynamic buffer, called the
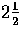 -D sketch.
-D sketch.
- is an extension of Marr and Poggio's work.
- uses the compatibility, uniqueness, and
continuity constraints proposed by Marr and Poggio.
- employs the coarse-to-fine multiresolution matching scheme.
- is an edge element-based system.
- assumes epipolar lines coinciding with the horizontal scanlines.
- depends mainly on the ordering constraint in the matching process.
The correspondence problem is thus
attempted as an optimization process in a 3-D
search space.
- selects interesting points (using the Moravec's interest operator).
- consists of various stages:
- preliminary matching: the matching is unconstrained
and hierarchical, the epipolar geometry is estimated
from prominent features that are successfully matched,
the epipolar constraint is then applied to a
hierarchical constrained matching scheme to get more matches.
- anchored matching:
continuity constraint is applied in this stage
to enforce smoothness on the disparities
of matches obtained from the previous stage.
This matching stage eliminates matches that
violate disparity smoothness, it also
matches the remaining interesting points
that do not yet have a match.
- postprocessing:
this final stage computes the 3-D coordinates
of matches and interpolates the 3-D data
for terrain model construction.
- employs a limit on allowable disparity gradients of 1,
a value that coincides with that reported for human
stereoscopic vision.
- employs the epipolar constraint -- only corresponding
scanline is considered. Search space is
limited to one-dimension.
- employs the uniqueness constraint.
- zero crossings serving as edge-like primitives
were extracted from each image.
- has been extended to geometrical modelling of objects
such as cylinders and cubes, and for
a robot arm to carry out pick-and-place tasks
- a line segment-based system. It has been later extended to
include curve segments by Deriche.
- matching process relies heavily on the epipolar constraint,
so the cameras must be pre-calibrated or rectified
(Ayache and Hansen, 1988. See also Appendix A).
- a measure of uncertainty is incorporated in
the representation of the estimated
3-D line segments (Zhang and Faugeras, 1992).
- the reconstructed scene has been used for
robot navigation (Ayache and Lustman, 1991).
- current research has been shifted to on-line camera
calibration (or self-calibration)
and non-metric representation of
3-D information (Faugeras 1992; Faugeras et al., 1992).


Next: Open problems
Up: Computer Vision IT412
Previous: Stereo matching
Robyn Owens
10/29/1997